What is an Insertion Electromagnetic Flowmeter
An Insertion Electromagnetic Flowmeter measures the average flow velocity of a fluid using electromagnetic methods, thereby obtaining the volumetric flow rate of the fluid. It is particularly suitable for large pipelines, solving the problems of difficult installation and high costs associated with pipeline-mounted electromagnetic flowmeters on large pipelines.
Working Principle of an Insertion Electromagnetic Flowmeter
Its working principle is based on Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction. In the flowmeter, the conductive medium within the measurement tube is equivalent to the conductive metal rod in Faraday’s experiment, and the two electromagnetic coils at the upper and lower ends generate a constant magnetic field. When the conductive medium flows, it generates an induced voltage, which is measured by two electrodes within the pipeline to calculate the flow rate of the fluid.

Characteristics of an Insertion Electromagnetic Flowmeter
Convenient Installation:
The Insertion Electromagnetic Flowmeter adopts pressure tapping and pressure installation technology, allowing installation without shutting down the system, greatly reducing installation difficulty and costs. It is suitable for various pipeline materials such as cast iron pipelines and cement pipelines, increasing its application flexibility.
Wide Applicability:
It can measure various conductive liquids, including corrosive liquids such as acids, alkalis, and salts, meeting the needs of different industrial scenarios. It is suitable for measuring large pipelines, solving the problems of difficult installation and high costs associated with pipeline-mounted electromagnetic flowmeters on large pipelines.
High-Precision Measurement:
It provides bidirectional high-precision measurement, ensuring the accuracy of flow data. It is an ideal choice for leak detection, capable of timely detection and localization of leak points.
High Reliability:
There are no movable or flow-restricting components inside the flowmeter, and there is almost no additional pressure loss during measurement, ensuring long-term operational stability. It is suitable for harsh working environments such as high temperatures, high pressures, and corrosive media.
Easy Maintenance:
The structural design of the Insertion Electromagnetic Flowmeter makes its maintenance simpler and more convenient. Real-time status monitoring can be performed through remote monitoring and diagnostic functions, reducing maintenance costs.
Cost-Effective:
Compared to other types of flowmeters, the Insertion Electromagnetic Flowmeter offers higher cost-effectiveness. It has low long-term operating costs and does not require frequent replacement or maintenance.
Application Scope of Insertion Electromagnetic Flowmeter
Pipeline Size:
Insertion Electromagnetic Flowmeters are particularly suitable for measuring the flow of large pipelines, solving the problems of difficult installation and high costs associated with pipeline-mounted electromagnetic flowmeters on large pipelines.
Fluid Types:
Capable of measuring various conductive liquids, including water, sewage, acids, alkalis, salt solutions, etc. It can also be used to measure liquids containing solid particles or fibers, as well as slurry fluids (such as paper pulp, mud, etc.).
Industrial Fields:
Used in process control, material ratio control, process optimization, and other aspects in industries such as chemicals, petroleum, metallurgy, and pharmaceuticals. Suitable for fluid measurement in the food and beverage industry, meeting hygienic requirements.
Environmental Conditions:
Suitable for harsh working environments such as high temperatures, high pressures, and corrosive media. It can operate stably for long periods in outdoor, underwater, or underground environments.
Special Applications:
Applicable for flow monitoring in urban water supply and drainage systems. Used for measuring the flow of natural water bodies such as rivers, lakes, and reservoirs in water conservancy projects. Used in the environmental protection field to monitor the discharge flow of wastewater and waste gas.
Accuracy and Reliability Requirements:
Applicable to situations requiring high-precision flow measurement, such as metering, filling, mixing, etc. Suitable for applications requiring high reliability of flowmeters, such as continuous production processes and flow monitoring in important pipeline networks.
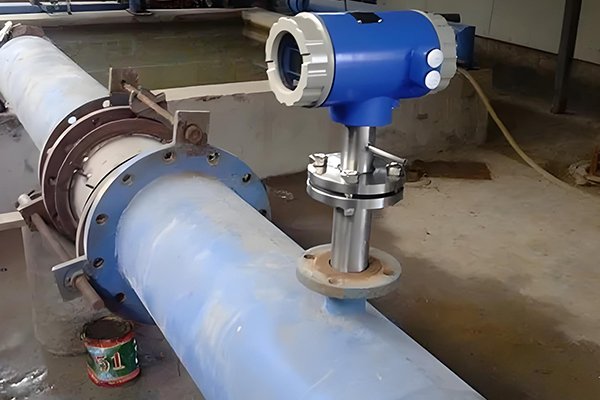

How to Install an Insertion Electromagnetic Flowmeter
Preparation Before Installation
Site Inspection: Conduct a thorough inspection and assessment of the installation site to understand parameters such as pipeline material, diameter, medium properties, flow velocity range, temperature, pressure, etc.
Flowmeter Selection: Select the appropriate flowmeter model and specification based on site conditions.
Tool Preparation: Prepare the necessary tools for installation, such as welding equipment, tapping machines, wrenches, screwdrivers, etc.
Inspect the Flowmeter: Conduct a visual inspection of the flowmeter to confirm that there are no defects such as damage, corrosion, or deformation. Additionally, check the flowmeter’s nameplate information, such as model, specification, range, accuracy, etc., to ensure consistency with the order.
Selection of Installation Location
Stable Flow Velocity Area: Choose a straight pipe section with stable flow velocity, no vortices, no bubbles, and no impurity accumulation as the installation location.
Avoid Interference: Avoid installing the flowmeter near pipeline bends, valves, pumps, and other equipment to prevent changes in fluid flow patterns from affecting measurement accuracy.
Vertical or Horizontal Installation:
Vertical Installation: When inserting the sensor into the pipeline, the angle with the vertical diameter of the pipeline cross-section should be less than 5°, suitable for measuring clean media with minimal pipeline vibration.
Horizontal Installation: Ensure that the electrode axis of the flowmeter is parallel to the horizontal plane to reduce errors caused by gravity.
Installation Steps
Clean the Pipeline: Clean the weld slag and burrs on the installation base of the measured pipeline to ensure a clean and tidy installation environment.
Close the Valve: Close the upstream flow control valve or use low-pressure water supply to ensure that the fluid in the pipeline is stationary during the installation process.
Install the Ball Valve: Install the DN50 ball valve onto the installation base, ensuring the long cavity of the ball valve is upward, and check if the ball valve can be fully opened and closed.
Install the Compression Device: Install the compression threaded seat, compression nut, and rubber sealing ring onto the ball valve and loosen the positioning nut.
Insert the Sensor: Insert the sensor rod through the ball valve into the measured pipeline, ensuring that the direction indicator of the sensor is aligned with the fluid flow direction.
Secure the Flowmeter: Secure the flowmeter and check its stability, ensuring that the sensor is tightly fitted to the inner wall of the pipeline to prevent leaks.
Cable Connection and Debugging
Cable Connection: Use specialized cables and connectors to connect the sensor to the converter, ensuring a secure and reliable connection. Check if the cable length and specification meet the requirements.
Debugging and Calibration: After installation, debug and calibrate the flowmeter. Set appropriate parameters such as range, zero point, damping time, etc., based on actual site conditions. Conduct sensitivity testing and repeatability testing to ensure the stability and reliability of measurement performance.

Maintenance of Insertion Electromagnetic Flowmeter
Regular Inspection and Cleaning
Visual inspection:
Inspect the appearance of the electromagnetic flowmeter at regular intervals (recommended every 1-3 months) to ensure there are no signs of visible mechanical damage or corrosion. Check the connecting components (such as seals and terminal blocks) to ensure they are secure and intact.
Clean the surface:
Regularly clean the surface of the electromagnetic flowmeter to prevent the accumulation of dust, grease, or other contaminants. Use a gentle cleaner and a soft cloth for cleaning, avoiding the use of highly corrosive chemicals.
Inspect the piping environment:
Check that the surroundings of the meter are clean, remove dirt and dust, and ensure no water or other substances enter the interior of the meter.
Maintenance of Electrodes and Sensors
Electrode Cleaning:
Regularly clean electrodes and sensor surfaces if the measurement medium is prone to fouling or depositing within the pipe walls. Use oil-free clean water for wiping, and avoid contact with oil-based substances to prevent electrode contamination and insulating lining damage.
Note: Shut down the system and drain the pipeline liquid before disassembly and cleaning for maintenance.
Check Electrode Resistance:
Disconnect the sensor-converter signal connection. When the sensor is filled with liquid, use a multimeter to measure resistance between electrodes and the ground terminal to check if they are within the manufacturer’s range and similar, indicating electrode integrity.
Inspect Sensor Cables:
Regularly inspect sensor power and transmission cables for damage or aging, and protect the rubber sheathing.
Calibration and Testing
Regular calibration:
Calibrate the electromagnetic flowmeter according to the manufacturer’s recommended interval (usually every 6 months to 1 year). During calibration, verify the accuracy of the output signal and actual flow, and adjust calibration parameters to ensure measurement accuracy.
Use testing equipment:
Tools such as insulation resistance testers and multimeters can be used to test the insulation resistance and electrode resistance of the flowmeter to assess the electrical performance and sensor status of the equipment.
Detailed Introduction of Electromagnetic Flowmeter



